SET vs SELECT is a common topic of discussion among SQL geeks and one of the most asked interview question. SET is used to assign a value to a variable and SELECT is used to assign a value or to select value from a variable/table/view etc.
Let’s see the usage of SET and SELECT in different scenarios.
Assigning scalar values
-- Query 1: Assigning scalar values Declare @set INT, @select INT SET @set=1 SELECT @select=1 SELECT @set AS 'Set', @select AS 'Select' GO
In the above query both SET and SELECT are used to assign a value to a variable.
Assigning values to multiple parameters
--Query 2: Assigning values to multiple parameters DECLARE @s1 INT, @s2 INT -- 2 SET statements SET @s1=1 SET @s2=2 -- 1 Select statement SELECT @s1=1, @s2=2
SET statement can assign value to a variable at a time. In order to assign values to two different variable two different SET statements are required. SELECT statement can assign values to multiple variables in a single go, as shown in above query. In this case, the SELECT statement performs better than SET.
Assigning values from a query
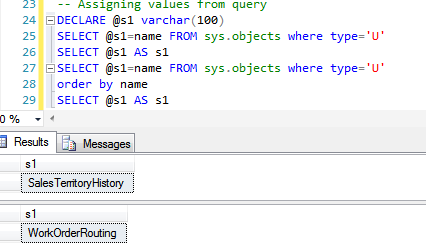
In below snapshot, SELECT statement is used to assign value to a variable from a select query. The SELECT statement assigns last value from the result set to the variable if the select query returns more than one result set.
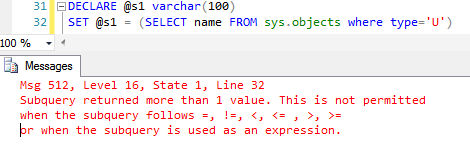
The SET statement errors out if the query returns more than one result set as shown below.
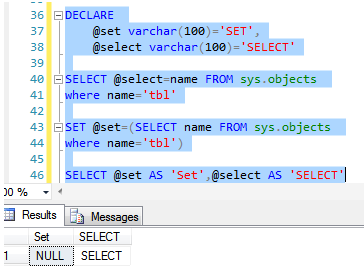
The SELECT statement doesn’t changes variable value if the query returns 0 rows. On the contrary, the SET statement sets variable to NULL, overriding previous value if the query returns 0 rows. This is shown in below snapshot.
Like us on FaceBook | Join the fastest growing SQL Server group on FaceBook

One Comment on “SET vs SELECT in SQL Server”